
| Part number: | UNC 5-6-6-BLUE/WHITE |
|---|---|
| Product classification: | Boxes |
| Manufacturer: | LMB Heeger, Inc. |
| description: | CABINET ALUM BL |
| Encapsulation: | - |
| Packing: | Bulk |
| Quantity: | 1 |
| RoHS: | 1 |
Quantity
Price
Total price
1
$76.8720
$76.8720
10
$67.2600
$672.6000
100
$63.9000
$6,390.0000


| TYPE | DESCRIPTION |
| Mfr | LMB Heeger, Inc. |
| Series | Uni-Cab |
| Package | Bulk |
| Product Status | ACTIVE |
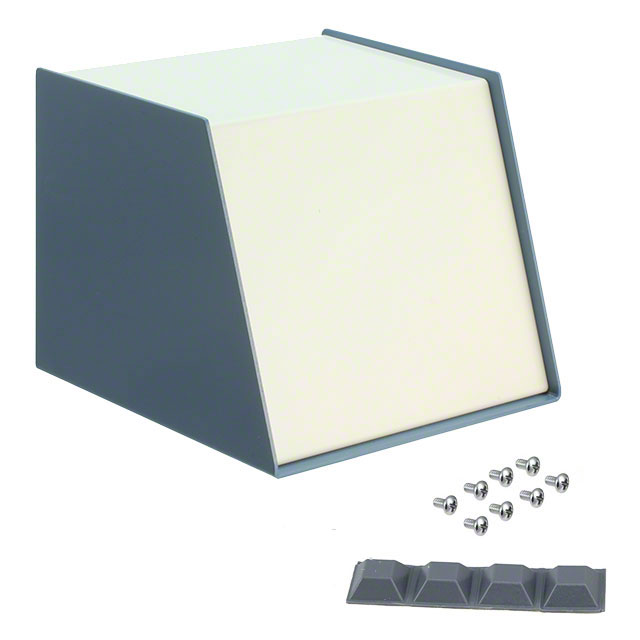
| Features | Separate Panel or Cover Thickness |
| Color | Blue, White |
| Size / Dimension | 6.000" L x 6.000" W (152.40mm x 152.40mm) |
| Material | Metal, Aluminum |
| Thickness | 0.090" (2.29mm) |
| Shipping Info | Shipped from Digi-Key |
| Height | 5.000" (127.00mm) |
| Design | Slanted Top |
| Container Type | Cabinet |
| Area (L x W) | 36.0in² (232cm²) |













